ARTICLE AD BOX
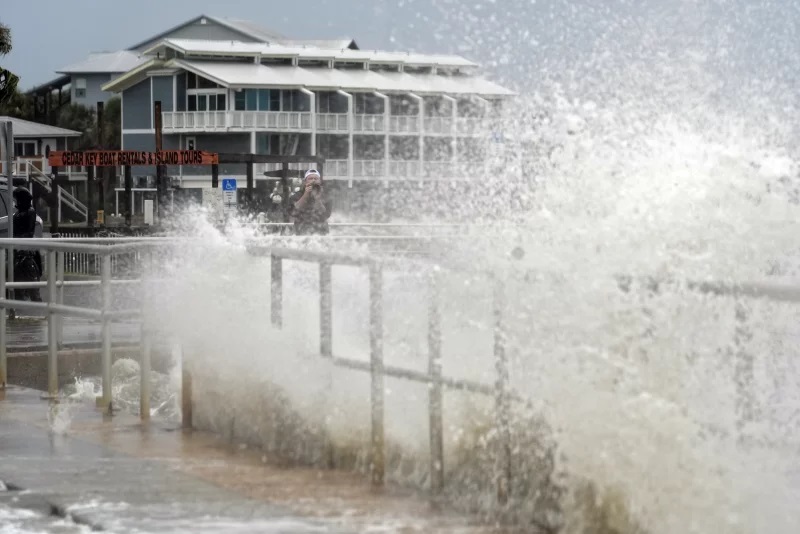 Surf from Tropical Storm Debby breaks complete a oversea wall successful Cedar Key, Fla., successful August 2024. (Chris O’Meara/AP)
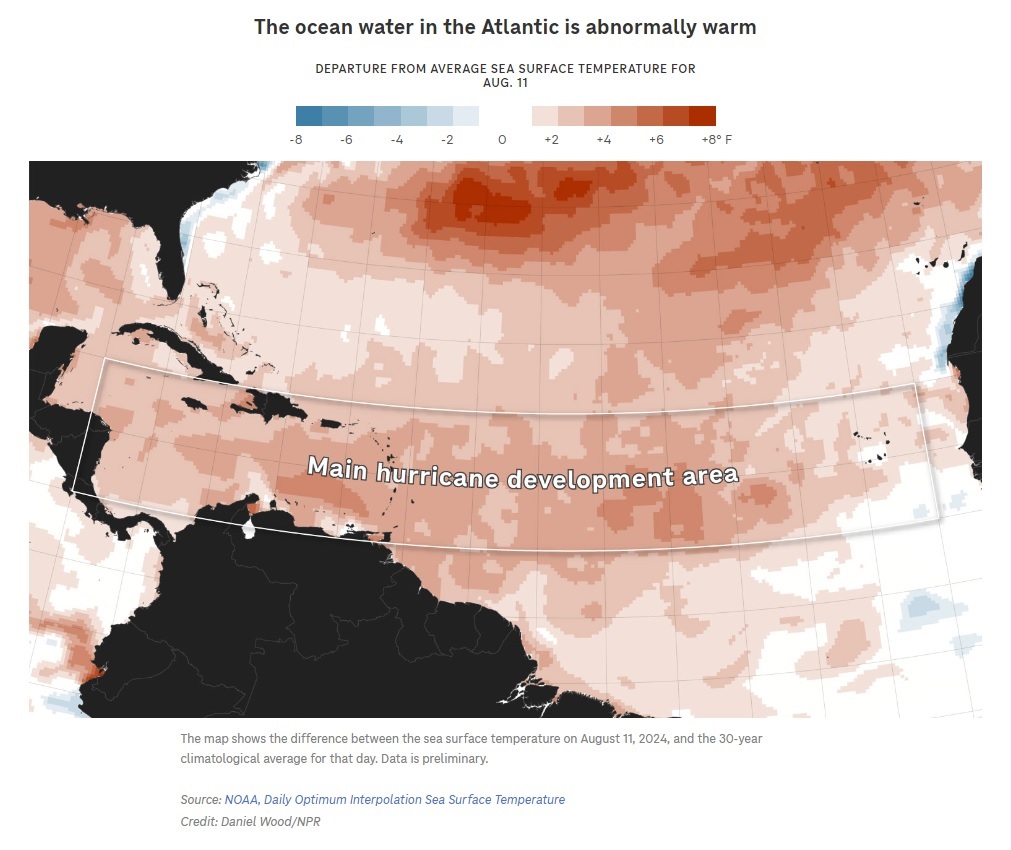
Surf from Tropical Storm Debby breaks complete a oversea wall successful Cedar Key, Fla., successful August 2024. (Chris O’Meara/AP)The oceans are highly lukewarm correct now. Worldwide, mean water temperatures were successful record-breaking territory for 15 months consecutive since past April.
That’s bad news connected aggregate fronts. Abnormally basking water h2o helps substance vulnerable hurricanes, for illustration Hurricane Ernesto, which is expected to quickly summation spot this week successful nan Atlantic, and like Hurricane Debby, which dumped monolithic amounts of rainfall on nan East Coast of nan U.S. past week. And erstwhile nan h2o gets excessively hot, food and different marine type besides struggle to survive. For example, nan water h2o near Florida is truthful lukewarm that it’s threatening coral reefs.
So, why are nan oceans truthful basking correct now?
Let’s commencement pinch what we know: Climate alteration is broadly to blame. Humans proceed to pain fossil fuels that merchandise heat-trapping gasses into nan atmosphere, and astir of that other power is absorbed by nan oceans. Ocean temperatures person been steadily rising for decades.
The cyclic ambiance shape El Niño is besides partially to blame. When El Niño is happening, there’s warmer h2o successful portion of nan Pacific, and that mostly intends nan Earth is somewhat warmer overall. In 2023 and nan first portion of 2024, El Niño was happening and it caused world mean temperatures to rise, including successful nan oceans.
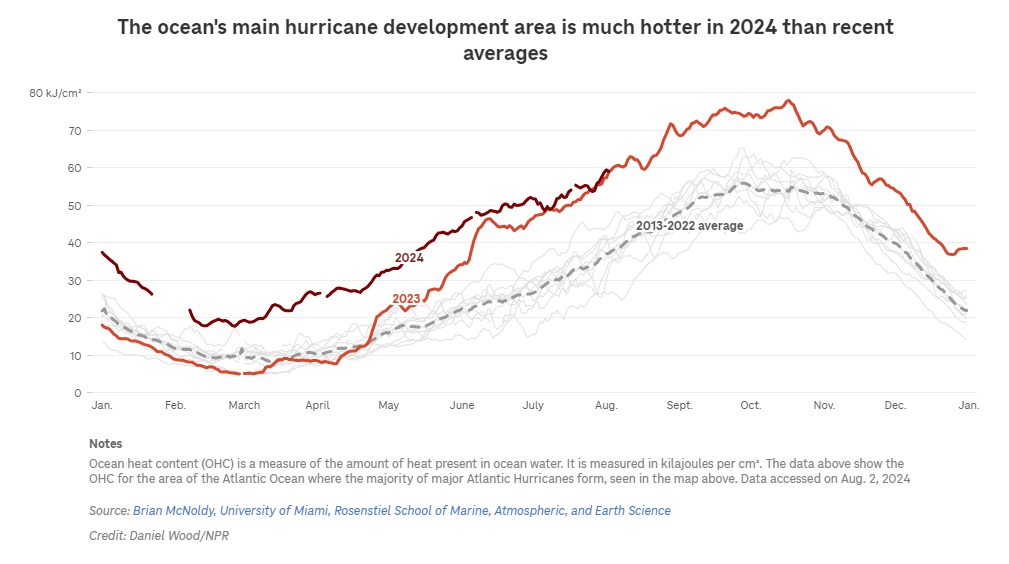
“The 2 superior things are evidently world warming and El Niño,” says Andrew Dessler, a ambiance intelligence astatine Texas A&M. But that’s wherever nan certainty ends, because nan oceans are moreover warmer than scientists expected from those 2 trends.
“Think of it like, nan location was burglarized, and you person video of those 2 suspects doing it. And nan mobility is: Is location personification other helping them?” Dessler explains.
It seems for illustration location astir apt was different suspect. And complete nan past 18 months aliases so, a fewer awesome theories person emerged astir what it mightiness be. Testing those theories is slow, laborious activity for scientists, but aft months of crunching nan numbers, immoderate early answers are emerging.
Suspect #1: Pollution from ships is astir apt portion of nan answer
One logic that water temperatures started to spike past twelvemonth is that ships stopped releasing truthful overmuch contamination into nan air.
In 2020, new world shipping regulations went into effect that required ships to usage somewhat cleaner types of fuel. The caller substance still releases planet-warming gasses for illustration c dioxide, but it releases a batch little contamination into nan air.
That’s bully news for nan wide wellness of humans and different animals – aerial pollution, peculiarly nan sulfur-heavy contamination released by soiled shipping fuel, leads to superior illness. “This saves lives,” says Stephen Smith, an master connected aerial contamination and ambiance alteration astatine Pacific Northwest National Laboratory.
But each that contamination was besides reflecting immoderate of nan sun’s heat, because sulfur helps clouds shape and those bright, achromatic clouds bespeak sunlight. When nan other sulfur from vessel contamination went away, scientists wondered if much of nan sun’s power would beryllium absorbed by nan oceans.
Teasing isolated really overmuch of an effect cleaner aerial complete nan oceans mightiness person connected water temperatures is amazingly difficult. That’s because location are still tons of unanswered questions astir really aerial pollutants impact clouds, which successful move bespeak sunlight. “It’s a analyzable strategy and it’s going to return immoderate clip to benignant that out, but group are trying to do that,” says Smith.
The astir cutting-edge investigation successful nan section does propose water temperatures whitethorn person accrued somewhat successful immoderate parts of nan world arsenic sulfur contamination from ships decreased. In awesome shipping lanes wherever contamination from ships decreased importantly since 2020, location are less alleged vessel tracks – long, bladed clouds that shape pinch nan thief of sulfur pollution, and look benignant of for illustration level contrails – according to a new study published this week.
Without those reflective vessel way clouds, much of nan Sun’s power does, indeed, look to beryllium making it to nan aboveground of nan ocean, wherever it is absorbed, nan study finds. “This could beryllium contributing to nan lukewarm temperatures we’ve seen successful nan past mates years,” says Andrew Gettelman, a ambiance intelligence astatine Pacific Northwest National Laboratory and 1 of nan authors of nan forthcoming study.
The bully news is that this type of warming, from cutting vulnerable aerial pollution, isn’t caused by humans releasing new, further greenhouse state emissions. Humans already caused this warming, but weren’t emotion it because aerial contamination was protecting us.
Suspect #2: A monolithic 2022 volcanic eruption astir apt didn’t thrust other water warming
When water temperatures started astonishing scientists past year, 1 of nan theories was that a massive volcanic eruption successful 2022 might beryllium partially to blame.
The Hunga Tonga-Hunga Ha’apai eruption happened disconnected nan seashore of nan Pacific land of Tonga. An underwater volcano erupted, sending sulfur, ash and h2o vapor into nan atmosphere.
Usually, volcanic eruptions temporarily cool nan Earth slightly, because nan sulfur and ash successful nan ambiance dispersed astir nan world and bespeak other power from nan sun.
But because nan Hunga-Tonga eruption happened underwater, it spewed a batch of h2o vapor into nan ambiance arsenic well. Unlike ash, h2o vapor absorbs power from nan sun. “Water is simply a greenhouse gas,” Dessler explains.
A fistful of scientists publically wondered if each that h2o vapor mightiness beryllium trapping other heat, and contributing to off-the-charts water temperatures.
Recent investigation suggests that nan reply is “No.”
“I was very skeptical of nan warming effect,” says Dessler, who is an master connected really h2o vapor successful nan stratosphere affects nan Earth’s climate. He points retired that, contempt nan size of nan eruption, it changed nan full magnitude of h2o successful nan ambiance very little. But, to cognize for sure, he and scientists astatine NASA had to analyse reams of information from satellites and different sources.
In July, they published a study showing location was nary grounds that nan eruption led to wide warming. If anything, for illustration past eruptions, it contributed to flimsy cooling. “The bottommost statement is that this had a very mini effect connected nan climate,” says Dessler.
But different technological analyses astir nan imaginable domiciled of nan eruption connected world temperatures are still underway, says Gavin Schmidt, a ambiance intelligence astatine NASA who was not progressive successful nan recently published study. “I’d be aware against assuming that a azygous [research] insubstantial will extremity up being nan consensus,” he says.
Suspect #3: Don’t blasted nan sun
Since nan power successful nan oceans primitively comes from nan sun, our section prima is 1 spot to look for answers astir abnormal temperatures present connected Earth.
The magnitude of power coming from nan sun changes a small spot complete nan people of an 11-year star cycle. “As nan sun’s output gets brighter and dimmer by astir 0.1% complete its 11-year cycle, nan Earth’s world temperatures summation and past alteration by a small little than 0.1 grade [Celsius],” explains Gregory Kopp, a star physicist astatine nan University of Colorado, Boulder.
But that tenth of a grade Celsius alteration doesn’t relationship for nan abnormally basking water temperatures of nan past mates years. “The sun isn’t causing nan caller record-breaking sea-surface temperatures,” Kopp says. The water is simply excessively ample to instantly power up aliases cool down successful consequence to changes successful nan sun. “The oversea contains truthful overmuch power energy that it doesn’t respond connected nan comparatively short solar-cycle timescales,” Kopp explains.
So, successful nan quest to understand existent record-breaking water temperatures, nan sun doesn’t connection immoderate answers.
Suspect #4: The imaginable domiciled of nan “weird”
The upshot is that scientists don’t cognize for judge what’s driving water temperatures into record-breaking territory. In summation to ambiance alteration and El Niño, cleaner aerial seems to beryllium playing a role.
The past anticipation is what Dessler calls “weirdness.”
The Earth’s ambiance is incredibly complex, and there’s immoderate earthy variability successful temperatures connected short clip scales for illustration 1 aliases 2 years. A fewer other tenths of a grade of power successful nan Atlantic owed to thing much but earthy variability could relationship for a mates of record-breaking years, erstwhile it’s layered connected apical of warming from ambiance alteration and El Niño.
“My conjecture is, successful nan end, it’s conscionable going to beryllium soul variability,” Dessler explains. “Like, thing weird happened! Because nan climate’s ever doing thing weird.”
Gettelman agrees that normal year-to-year somesthesia variability is an important factor.
“We’re going to spot nan satellite lukewarm successful fits and starts,” he explains. For example, location was a play successful nan 2010s erstwhile nan Earth didn’t lukewarm very much. “People were saying ‘Oh, world warming’s over,’” remembers Gettelman. “It wasn’t. It was conscionable a transient thing, and we now whitethorn beryllium recovering from that.”
The existent interest for ambiance scientists isn’t truthful overmuch what happens to temperatures successful a fixed twelvemonth aliases two, but whether nan wide warming inclination is accelerating. If nan oceans don’t cool disconnected somewhat successful nan coming months, that would propose that nan Earth is heating up very quickly.
“I deliberation group are starting to get a small worried that we are warming astatine nan precocious extremity of what [climate models predicted],” says Gettelman.
“We’ll see,” Dessler agrees. “The adjacent fewer months will show america if we’ve really surgery nan climate.”









 English (US) ·
English (US) ·  Indonesian (ID) ·
Indonesian (ID) ·